HVAC - Introduction to Heat Pumps
In this module, we take an introductive look at air-source heat pumps in HVAC systems and how they move heat. Their benefits and energy efficiency advantages are discussed, as well as best practices for determining ideal sizing and design for installation. Lastly, calculations are detailed in order to know how to make a financial case for the purchase and installation of efficient air-sourced heat pumps.
Curriculum
-
Remember
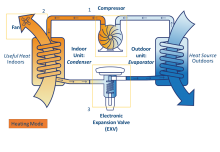
- Describe what an air source heat pump is and what it can be used for.
- Remember key terms related to sizing and design of heat pumps.
- Know the customer benefits of ASHPs.
: Introduction to Heat Pumps - RememberLecture Notes
: Introduction to Heat Pumps - Problem Set 1.1Problem Set
: Introduction to Heat Pumps - Problem Set 1.2Problem Set
-
Understand
- Understand how a heat pump moves heat.
- Understand the different types of heat pumps.
- What are the different heat pump options when looking for alternatives for homes that are currently heated by a gas furnace or boiler?
- Understand the market trends for heat pumps and the benefits of switching to heat pumps in existing homes.
- Understand the business case for ASHP installation services.
: Introduction to Heat Pumps - UnderstandLecture Notes
: Introduction to Heat Pumps - Problem Set 2.1Problem Set
: Introduction to Heat Pumps - Problem Set 2.3Problem Set
: Introduction to Heat Pumps - Problem Set 2.4Problem Set
-
Apply
- What should a person consider before installing an air source heat pump?
- What should an HVAC installer consider about the ductwork and condensate drain in an existing home before installing a heat pump?
- Be able to compare the operating costs of ASHPs and fossil fuel heating systems.
: Introduction to Heat Pumps - ApplyLecture Notes
: Introduction to Heat Pumps - Problem Set 3.1Problem Set
: Introduction to Heat Pumps - Problem Set 3.2Problem Set
: Introduction to Heat Pumps - Problem Set 3.3Problem Set
Teaching Materials

HVAC Quality Installation
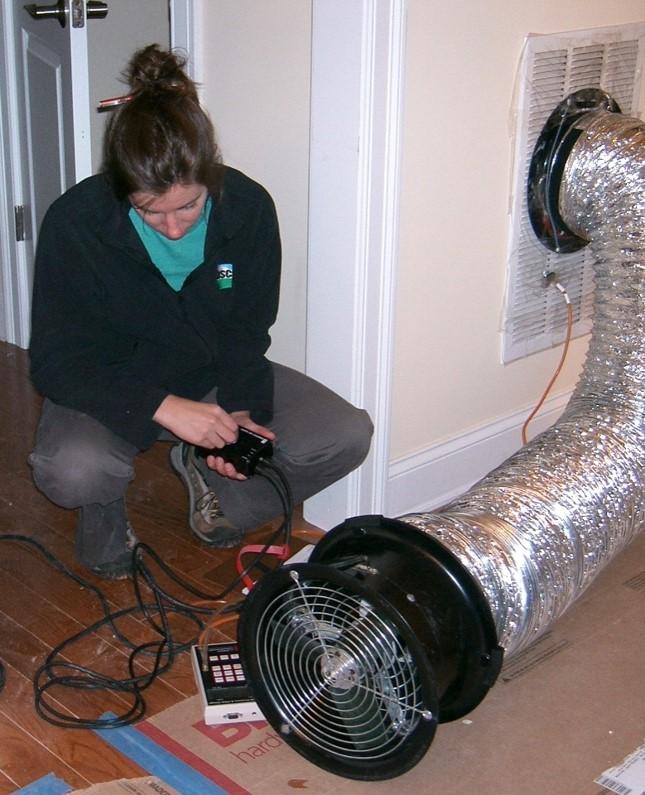
Quality installation—that is, installation by certified professionals who follow industry standards and manufacturers’ recommendations—will save energy, improve equipment performance and safety, and ensure the system’s longevity. Professional HVAC installers follow recognized industry standards like those set by the Air Conditioning Contractors of America (ACCA) for proper design, sizing, installation, charging, and commissioning of HVAC equipment.
More than half of all HVAC systems in US homes are believed to perform poorly due to one or more installation issues, which includes oversizing of furnaces and air conditioners and improperly designed, sized, and installed duct systems. Such systems will not operate as efficiently as they should; they also may not last as long as they could.
The components of quality installation include proper sizing of equipment and component matching; ensuring the correct amount of refrigerant, or correct refrigerant charge; ensuring adequate airflow to match refrigerant capacity; and properly sealing ducts to minimize leaks. Savings from improved installations may range from 18% to 36% for air conditioners and heat pumps and 11% to 18% for furnaces.