HVAC
HVAC Geothermal Heat Pumps
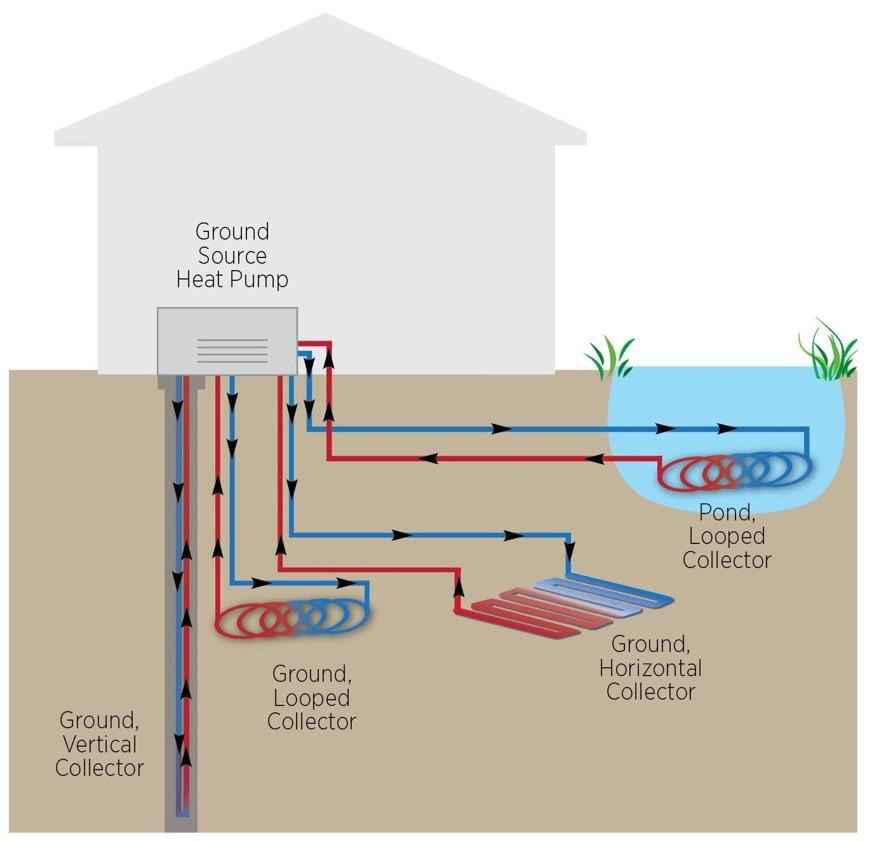
A ground-source heat pump is an electric heat pump that exchanges heat with the ground or groundwater. Ground source heat pumps (often called geothermal heat pumps) take advantage of the fact that the temperature of the earth (below the surface) remains fairly constant.
The average single-family home spends half of its energy use on heating and cooling. Because heat is exchanged with the ground rather than with the outside air, which has more erratic temperatures, ground-source heat pumps are a very efficient source of heating and cooling year-round. These pumps can have efficiencies of 300% to 600%, compared to 175% to 250% for central ducted air-source heat pumps.
A geothermal heat pump exchanges heat with the earth via a system of pipes called a loop, which is buried in the ground (or sometimes, in a pond). Water or a mixture of water and antifreeze circulates through the pipes, exchanging heat with the earth. In winter, heat moves from the ground into the heat exchanger and into the home; in summer, the process is reversed, and heat is released from indoor air into the heat exchanger and ultimately, back into the ground. This heat can also be used to heat domestic water.