HVAC
HVAC Whole-House Ventilation
Whole-house ventilation systems use one or more fans and duct systems to exhaust stale air and/or supply fresh air to the house. By providing a continuous supply of fresh air, these systems dilute potential contaminants throughout the home.
Whole-house ventilation systems meet the ventilation levels required by building codes or national home performance programs.
Airtight homes save lots of energy, but pollutants can also accumulate if there is not adequate exchange with fresh outdoor air. Local exhaust ventilation (kitchen and bathroom exhaust fans) only run intermittently to remove contaminants near where they are generated. Whether new or existing, all energy-efficient homes require whole-house mechanical ventilation to maintain good indoor air quality.
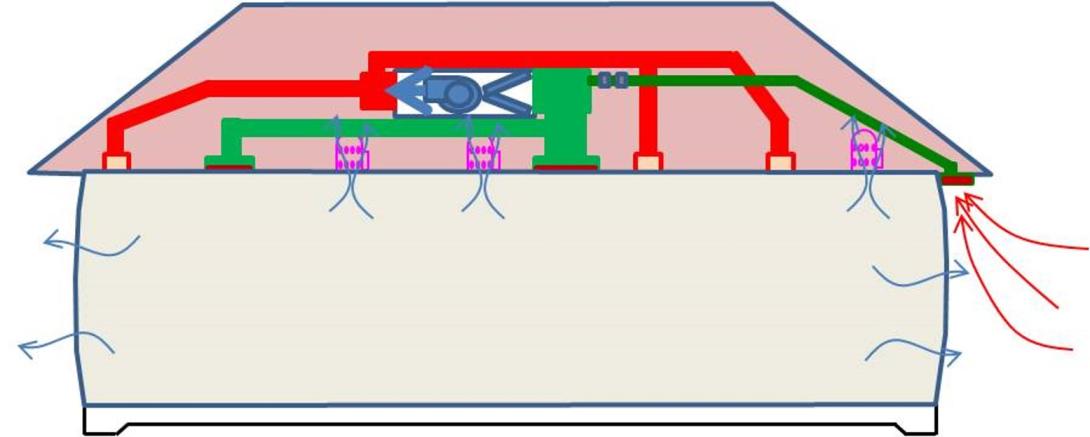
There are four types of whole-house ventilation systems:
- Exhaust ventilation systems mechanically exhaust air from the house. Makeup air infiltrates through leaks in the building shell and through intentional vents.
- Supply ventilation systems use a fan to pressurize the home, forcing outside air into the building. Air leaks outside through holes in the shell, bath, range fan ducts, and intentional vents.
- Balanced ventilation systems introduce and exhaust equal volumes of fresh outside air and inside air.
- Energy recovery ventilation systems ventilate a home while minimizing energy loss via heat transfer.